Home energy monitoring systems are transforming how we manage our energy consumption. These systems, ranging from simple smart plugs to comprehensive whole-home monitors, offer valuable insights into our energy usage, helping us identify wasteful habits and make informed decisions to reduce our carbon footprint and lower our bills. Understanding how these systems work, their features, and their potential benefits is key to harnessing their power for a more sustainable and cost-effective lifestyle.
From tracking real-time energy usage to providing detailed historical data analysis, these systems empower homeowners to take control of their energy spending. They allow for easy identification of energy-hungry appliances, facilitating targeted energy-saving strategies. Integration with smart home platforms further enhances their functionality, allowing for automated adjustments and seamless control.
Types of Home Energy Monitoring Systems
Home energy monitoring systems offer valuable insights into your energy consumption, empowering you to make informed decisions about energy efficiency and cost savings. Several types of systems cater to different needs and budgets, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right system depends on your technical skills, home setup, and desired level of detail.
Comparison of Home Energy Monitoring Systems
The following table compares three common types of home energy monitoring systems: smart plugs, whole-home energy monitors, and sub-metering systems. Understanding their features, costs, and installation processes is crucial for making an informed purchase.
| System Type | Features | Cost Range | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Plugs | Monitor energy usage of individual appliances; remote control; scheduling capabilities; often integrate with smart home ecosystems. | $10 – $50 per plug | Pros: Affordable, easy to install, provides granular appliance-level data. Cons: Limited to plugged-in devices; may not provide whole-home overview; accuracy can vary. |
| Whole-Home Energy Monitors | Measure overall energy consumption; display real-time usage; identify energy-intensive appliances; often provide historical data and energy usage reports; some offer advanced features like energy cost calculations and demand response capabilities. | $50 – $300 | Pros: Comprehensive overview of home energy usage; easy to identify high-consumption areas. Cons: More expensive than smart plugs; installation may require some technical knowledge (depending on the model); accuracy depends on proper installation and calibration. |
| Sub-metering Systems | Measure energy consumption of specific circuits or areas of the home; often used for identifying energy usage patterns in different rooms or sections of a house; can help pinpoint energy leaks or inefficient appliances within specific areas. | $100 – $1000+ | Pros: Highly accurate circuit-level data; allows for detailed analysis of energy consumption by area; can be beneficial for larger homes or those undergoing energy efficiency upgrades. Cons: Expensive; complex installation usually requiring professional help; may require significant electrical work. |
Accuracy and Functionality, Home energy monitoring systems
The accuracy and functionality of home energy monitoring systems vary significantly depending on the type of system and its features. Smart plugs generally offer good accuracy for individual appliances but may not be as precise for the whole house. Whole-home energy monitors provide a more holistic view but may not capture the fine-grained data offered by sub-metering systems. Sub-metering systems, while highly accurate, are more complex and costly.
The level of detail and accuracy you need should guide your system choice. For example, if you primarily want to track the energy use of individual appliances like your refrigerator or gaming console, smart plugs are sufficient. However, for a comprehensive understanding of your home’s energy profile, a whole-home monitor or even a sub-metering system may be more suitable.
Installation Process
Installation processes vary greatly depending on the system type. Smart plugs are the easiest to install, simply requiring plugging them into an outlet and connecting them to your Wi-Fi network. Whole-home energy monitors usually involve connecting them to your electrical panel, often a DIY task for those comfortable working with electrical systems, but professional installation is always recommended for safety.
Sub-metering systems typically require extensive electrical work and professional installation, due to the need to install additional metering equipment in your electrical panel and potentially run new wiring. Always prioritize safety and consider professional installation if you lack the necessary electrical expertise.
Key Features and Functionality
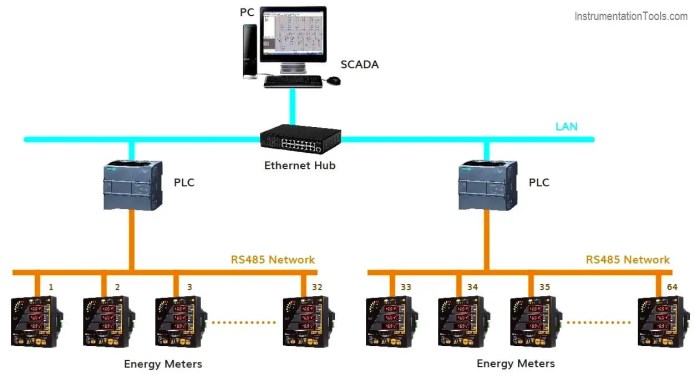
Source: instrumentationtools.com
Home energy monitoring systems offer a range of features designed to provide homeowners with a comprehensive understanding of their energy consumption patterns. These systems go beyond simply showing your current energy usage; they provide tools for analysis, prediction, and ultimately, cost savings. The core functionality revolves around tracking, analyzing, and acting upon your energy data.Real-time energy usage tracking, historical data analysis, and actionable alerts are fundamental aspects of these systems.
They empower users to make informed decisions about their energy consumption, identify energy-intensive appliances, and ultimately reduce their energy bills. The ability to access this information remotely adds further convenience and control.
Real-time Energy Usage Tracking and Historical Data Analysis
Real-time monitoring displays your current energy usage, often broken down by circuit or appliance, providing an immediate snapshot of your home’s energy consumption. This allows for immediate adjustments to energy-intensive activities. Coupled with this is the ability to review historical data, typically presented as graphs and charts showing energy use over various timeframes (daily, weekly, monthly, yearly). This historical perspective helps identify trends, seasonal variations, and the impact of changes in energy usage habits.
For example, comparing energy usage before and after switching to energy-efficient light bulbs provides clear evidence of the savings achieved.
Energy Consumption Alerts and Remote Access
Many systems offer customizable alerts, notifying users of unusually high energy consumption. This proactive approach helps identify potential problems, such as a malfunctioning appliance or a forgotten appliance left running. Remote access capabilities allow users to monitor and manage their energy usage from anywhere with an internet connection, providing unparalleled convenience and control. Imagine being able to check your home’s energy consumption while on vacation and remotely adjusting the thermostat to save energy.
Integration with Smart Home Platforms and Other Smart Devices
Integrating a home energy monitoring system with a smart home platform (such as Google Home or Amazon Alexa) allows for seamless control and automation. This integration enables features like automated energy-saving routines, triggered by specific events or times. For instance, smart lights can automatically turn off when a room is unoccupied, and smart thermostats can adjust temperatures based on occupancy and energy usage patterns.
Home energy monitoring systems are great for understanding your household’s power consumption. Want to take control of your energy usage in the kitchen? Check out these cool Voice-controlled kitchen gadgets that can help you manage appliances more efficiently, which in turn can be tracked by your home energy monitoring system, helping you save money and reduce your carbon footprint.
Furthermore, integrating with smart appliances allows for precise tracking of individual appliance energy consumption, providing granular insights into energy usage. For example, a smart refrigerator can report its daily energy consumption, allowing users to identify if it’s operating efficiently.
Identifying Energy-Consuming Appliances and Pinpointing Areas for Potential Energy Savings
By analyzing energy usage data, these systems can pinpoint specific appliances or circuits responsible for the highest energy consumption. This allows homeowners to focus their efforts on areas with the greatest potential for energy savings. For example, the system might identify a particular circuit consistently drawing high power, leading the homeowner to investigate the appliances connected to that circuit, potentially revealing a faulty or inefficient device.
This detailed information empowers informed decision-making regarding appliance upgrades or behavioral changes to reduce energy waste.
Data Analysis and Visualization
Home energy monitoring systems provide a wealth of data, but understanding this data is key to its usefulness. Effective data analysis allows you to identify energy consumption patterns, pinpoint energy-guzzling appliances, and ultimately, reduce your energy bills. This section explores how to interpret the data presented by your system and utilize it for significant energy savings.Data analysis involves identifying trends and patterns in your energy usage.
This can be done by examining daily, weekly, monthly, or even yearly consumption data. Look for peaks and valleys in energy use to understand when your home consumes the most and least energy. Identifying these patterns allows for targeted adjustments to your energy consumption habits. For example, consistently high energy consumption during evening hours might indicate excessive use of lighting or entertainment systems.
Interpreting Energy Consumption Data
Analyzing your energy data requires understanding the different metrics presented by your monitoring system. Total energy consumption (typically measured in kilowatt-hours, or kWh) provides an overall picture of your energy use. Peak usage time indicates the period when your energy consumption is highest. Finally, an appliance breakdown shows the individual energy consumption of various appliances in your home.
By combining these data points, you can create a comprehensive view of your energy usage and identify areas for improvement. For instance, a high daily energy consumption coupled with a peak usage time during the late afternoon could suggest inefficient air conditioning usage. Analyzing the appliance breakdown might then reveal that the air conditioner is the primary contributor to high energy consumption during this time.
Sample Weekly Energy Consumption Report
The following table provides a sample report visualizing energy consumption data over a week. Remember, these figures are illustrative examples and your actual consumption will vary depending on your household’s energy usage habits and the size and efficiency of your home appliances.
| Day | Total Energy Consumption (kWh) | Peak Usage Time | Appliance Breakdown (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | 15 | 6:00 PM – 8:00 PM | AC: 5, Lighting: 3, Refrigerator: 2, Other: 5 |
| Tuesday | 12 | 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | AC: 4, Lighting: 2, Refrigerator: 2, Other: 4 |
| Wednesday | 18 | 12:00 PM – 2:00 PM | AC: 7, Oven: 4, Refrigerator: 2, Other: 5 |
| Thursday | 14 | 6:00 PM – 8:00 PM | AC: 5, TV: 3, Refrigerator: 2, Other: 4 |
| Friday | 16 | 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | AC: 6, Lighting: 3, Refrigerator: 2, Other: 5 |
| Saturday | 20 | 1:00 PM – 3:00 PM | AC: 8, Washer/Dryer: 6, Refrigerator: 2, Other: 4 |
| Sunday | 13 | 7:00 PM – 9:00 PM | AC: 4, Lighting: 2, Refrigerator: 2, Other: 5 |
Strategies for Reducing Energy Consumption
Analyzing your energy data allows for targeted strategies to reduce consumption. For example, if the data consistently shows high energy use during specific times, you can adjust your usage habits. If your peak usage occurs during peak electricity pricing periods, shifting energy-intensive tasks to off-peak times can lead to significant savings. Furthermore, identifying appliances that consume a disproportionate amount of energy allows for targeted improvements.
This might involve replacing inefficient appliances with energy-efficient models, or simply being more mindful of their usage. For instance, consistently high AC usage might warrant checking the unit’s efficiency and ensuring proper insulation in your home. Regular maintenance of appliances can also significantly reduce energy consumption.
Cost and Return on Investment
Source: com.my
Investing in a home energy monitoring system requires careful consideration of both upfront costs and potential long-term savings. The initial investment can vary significantly depending on the type of system chosen, its features, and the complexity of installation. However, the potential for reduced energy bills and increased home efficiency often makes it a worthwhile expenditure.The initial cost of a home energy monitoring system encompasses the purchase price of the hardware and any associated installation fees.
Simple plug-in energy monitors might cost as little as $20-$50, while more sophisticated whole-home systems, including professional installation, can range from $200 to over $1000. Factors like the number of sensors, smart features, and the level of professional installation required all contribute to the overall cost. DIY installation generally reduces labor costs, but requires some technical expertise.
Initial Costs of Home Energy Monitoring Systems
A breakdown of the initial costs is crucial for informed decision-making. The price varies dramatically depending on the system’s complexity and features. A basic, single-outlet monitor might cost only a few tens of dollars, whereas a comprehensive system integrating smart thermostats, smart plugs, and advanced data analysis software could cost several hundred or even thousands of dollars. Professional installation adds to the cost, potentially doubling or tripling the price of the hardware itself.
For example, a simple smart plug might cost $25, while a full smart home energy management system with professional installation could cost $800-$1200.
Potential Long-Term Cost Savings
Using a home energy monitoring system can lead to substantial long-term cost savings through increased energy efficiency. These savings stem from better understanding and control of energy consumption.
- Reduced energy bills: By identifying energy-intensive appliances and habits, homeowners can make informed decisions to reduce consumption, leading directly to lower electricity bills.
- Targeted energy efficiency improvements: The data provided by the system can highlight areas where improvements are most needed. This might involve replacing inefficient appliances, upgrading insulation, or sealing air leaks.
- Avoidance of costly repairs: Early detection of potential problems, such as a constantly running appliance, can prevent more expensive repairs down the line.
- Reduced peak demand charges: Some utility companies charge more during peak demand periods. Energy monitoring systems can help manage energy use to minimize these charges.
Factors Influencing Return on Investment (ROI)
Several factors influence how quickly a homeowner sees a return on their investment in a home energy monitoring system. These factors include the initial cost of the system, the level of energy consumption before and after implementation, electricity prices, and the homeowner’s commitment to making energy-saving changes.For example, a homeowner with high energy consumption in a region with high electricity prices will likely see a faster ROI than someone with low consumption in a region with low prices.
Similarly, a homeowner who actively uses the data provided by the system to make changes in their energy habits will see a greater return than someone who simply installs the system and does not change their behavior. The longevity of the system is also a factor; a system that lasts for many years will have a lower overall cost per year of use.
The ROI can be estimated by comparing the annual cost savings to the initial investment cost. A simple calculation might be:
Annual Savings / Initial Investment Cost = Approximate Annual ROI
However, a more detailed analysis considering factors like system lifespan and inflation is recommended for a complete picture.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Smart home energy monitoring systems, while offering significant benefits in terms of energy efficiency and cost savings, also introduce potential security and privacy risks. These systems collect and transmit a considerable amount of data about your energy consumption habits, which could potentially be misused if not properly secured. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for protecting your personal information and ensuring the security of your home network.The primary concern revolves around the potential for unauthorized access to your system and the data it collects.
Home energy monitoring systems are great for tracking your usage and identifying areas for improvement. For example, you might find that upgrading your kitchen cabinets, perhaps choosing stylish new options like those found at Cabinet door designs , doesn’t significantly impact your energy bill, but replacing old appliances certainly will. Ultimately, understanding your energy consumption is key to making informed decisions about home improvements.
This could range from simple data breaches revealing your energy usage patterns to more serious scenarios involving manipulation of your home’s energy systems or even identity theft. Furthermore, the data collected can reveal sensitive information about your lifestyle and daily routines, potentially making you a target for criminals.
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
A major concern is the vulnerability of these systems to hacking and data breaches. Weak passwords, outdated software, and insecure network configurations can all create entry points for malicious actors. A successful breach could expose your energy consumption data, potentially revealing information about your presence or absence at home, your sleep schedule, and even the types of appliances you use.
Home energy monitoring systems offer valuable insights into your household’s power consumption, helping you identify areas for savings. But energy efficiency is just one piece of the puzzle; a truly secure smart home needs robust protection, which is why integrating your system with features like those found in Smart home security is a great idea. This holistic approach ensures not only energy savings but also peace of mind, making your home safer and more efficient.
This information could be used for targeted burglaries or other malicious activities. For example, a hacker could identify periods of inactivity, indicating an opportune time to break into a home. Another example would be an attacker exploiting vulnerabilities to manipulate smart thermostats, potentially causing discomfort or even damage to the property.
Mitigation Strategies
Several measures can significantly mitigate these risks. Using strong, unique passwords for each connected device is paramount. This prevents attackers from using the same credentials across multiple systems. Regularly updating the firmware of your energy monitoring system and its associated components is also critical, as updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities. Ensuring your home network is secured with a strong password and up-to-date firewall is also essential.
Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and further protect your data. Finally, regularly reviewing the security settings of your energy monitoring system and understanding the data it collects is crucial for proactive protection.
Protecting Personal Data
Protecting personal data collected by home energy monitoring systems requires a multi-faceted approach. Understanding the data collected by your system and its intended use is the first step. Many systems allow you to adjust data collection settings, allowing you to control the level of detail being tracked. Reviewing your system’s privacy policy and understanding how your data is stored, used, and protected is also crucial.
Opting out of data sharing features whenever possible further limits the potential for misuse of your information. Regularly checking your system’s logs for any suspicious activity can help identify potential breaches early on.
Future Trends and Innovations
Home energy monitoring systems are rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and a growing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability. The integration of artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and renewable energy sources is transforming how we monitor and manage our energy consumption, paving the way for smarter, more sustainable homes. This section explores these exciting developments and their potential impact.The convergence of several technological advancements is leading to increasingly sophisticated home energy monitoring systems.
AI-powered energy management, for example, allows for personalized energy consumption recommendations based on individual household patterns and preferences. Predictive analytics helps anticipate energy needs and optimize energy use proactively, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. Meanwhile, seamless integration with renewable energy sources, like solar panels and wind turbines, provides a comprehensive view of energy production and consumption, facilitating better decision-making.
Home energy monitoring systems can help you understand your household’s energy consumption, pinpointing areas for improvement. For example, you might discover that your appliances, like Automated coffee makers , are using more energy than you’d expect. By identifying these energy hogs, you can make informed decisions about usage and potentially save money on your energy bills, making your home more efficient overall.
AI-Powered Energy Management
AI is revolutionizing home energy monitoring by enabling personalized energy recommendations and automated adjustments. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical energy usage data, identifying patterns and anomalies to predict future consumption. This allows systems to proactively adjust energy settings, such as thermostat temperatures or appliance usage, to optimize energy efficiency. For example, an AI-powered system might learn that a household typically consumes more energy during peak hours and automatically shift energy-intensive tasks to off-peak periods, resulting in lower energy bills.
These systems can also learn user preferences and adjust energy use accordingly, offering a customized and highly efficient experience.
Predictive Analytics for Energy Optimization
Predictive analytics uses historical data and advanced algorithms to forecast future energy consumption. By analyzing factors such as weather patterns, occupancy schedules, and appliance usage, these systems can accurately predict energy needs. This allows homeowners to proactively manage energy use, preventing unexpected spikes in consumption and reducing overall energy costs. For instance, a system might predict a surge in energy demand due to an upcoming heatwave and automatically pre-cool the house during off-peak hours, preventing energy waste during peak demand.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
The integration of home energy monitoring systems with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, is crucial for achieving energy independence and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. These systems provide a holistic view of energy production and consumption, enabling homeowners to optimize their energy usage based on real-time data from renewable sources. For instance, a system might automatically adjust appliance usage to maximize the utilization of solar energy generated during peak sunlight hours, minimizing reliance on the grid.
This integration fosters a more sustainable energy ecosystem within the home.
Home energy monitoring systems help you understand your energy usage, allowing for informed decisions about efficiency. This can even extend to things like optimizing the use of appliances, such as sterilizing devices; for example, you might consider using UV light sanitizers for better hygiene, but only when energy consumption is low to minimize overall impact on your energy bill.
Ultimately, smart energy management is key to both cost savings and a more sustainable lifestyle.
Potential Future Developments in Home Energy Monitoring Systems
The future of home energy monitoring holds immense potential. Several advancements are on the horizon, poised to significantly impact energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Enhanced AI capabilities: More sophisticated AI algorithms will enable even more accurate energy predictions and personalized recommendations, leading to greater energy savings.
- Improved data visualization: More intuitive and user-friendly dashboards will make it easier for homeowners to understand and interpret their energy usage data, empowering them to make informed decisions.
- Wider device integration: Future systems will integrate with a broader range of smart home devices, providing a comprehensive overview of energy consumption across the entire household.
- Blockchain technology for secure data management: Blockchain can enhance data security and privacy, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of energy usage data.
- Advanced energy storage solutions: Integration with advanced battery storage systems will enable homeowners to store excess renewable energy for later use, maximizing the utilization of renewable sources.
- Gamification and behavioral nudges: Interactive features, such as gamification and personalized feedback, will encourage energy-conscious behavior and promote greater energy efficiency.
Impact on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
The innovations discussed above have the potential to significantly improve energy efficiency and promote sustainability. By enabling proactive energy management, predictive analytics, and seamless integration with renewable sources, these systems can help reduce energy consumption, lower energy bills, and minimize reliance on fossil fuels. This contributes to a greener environment and a more sustainable future. For example, widespread adoption of AI-powered systems could lead to a substantial reduction in overall energy consumption at a community level, mitigating the effects of climate change.
Similarly, the integration of renewable energy sources coupled with effective monitoring systems can help accelerate the transition to a cleaner energy future.
Ultimate Conclusion
Ultimately, investing in a home energy monitoring system is an investment in both cost savings and environmental responsibility. By providing detailed insights into energy consumption patterns, these systems empower homeowners to make informed decisions, reduce waste, and lower their energy bills. As technology continues to evolve, these systems promise even greater efficiency and integration with other smart home technologies, paving the way for a more sustainable and connected future.
User Queries: Home Energy Monitoring Systems
What’s the difference between a smart plug and a whole-home energy monitor?
A smart plug monitors the energy usage of a single appliance, while a whole-home monitor tracks energy consumption for your entire house.
How accurate are these systems?
Accuracy varies depending on the system and its sensors. Generally, they provide a good estimate of energy usage, though minor discrepancies may occur.
Can I install a home energy monitoring system myself?
Many systems are DIY-friendly, but some, especially whole-home monitors, may require professional installation for optimal performance and safety.
Are my data secure with these systems?
Reputable manufacturers employ security measures to protect your data. However, it’s essential to use strong passwords, keep software updated, and choose systems with robust security features.
How much can I save with a home energy monitoring system?
Savings vary depending on your energy usage habits and the system’s effectiveness in identifying areas for improvement. However, even small changes can lead to significant long-term cost reductions.



