Smart home networks are transforming how we live, offering convenience and control over our homes through interconnected devices. From automated lighting and temperature control to security systems and entertainment, these networks seamlessly integrate technology into our daily routines. But building a reliable and secure smart home network requires careful planning and understanding of the underlying technologies and potential vulnerabilities.
This exploration delves into the key aspects of smart home networks, covering everything from network topologies and security protocols to interoperability challenges and future trends.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of smart home network technologies, security best practices, and the considerations for seamless integration and optimal performance. We will explore various communication protocols, discuss the importance of robust security measures, and examine the challenges and opportunities presented by the evolving landscape of smart home technology. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to design, implement, and manage a secure and efficient smart home network.
Defining Smart Home Networks
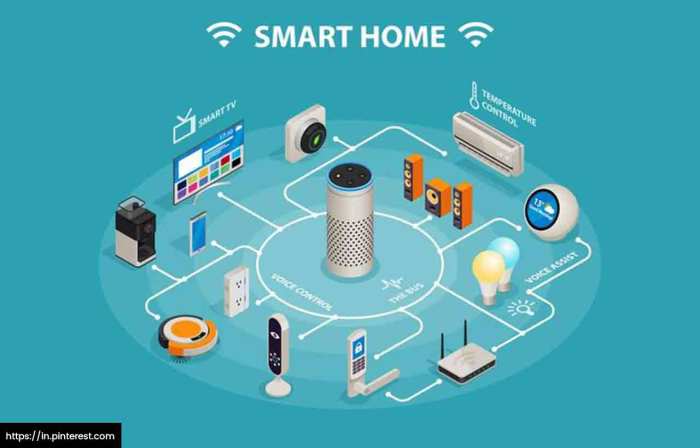
A smart home network is the backbone of a connected home, enabling communication between various smart devices and appliances. It allows for automated control, remote monitoring, and seamless integration of different systems, enhancing convenience, security, and energy efficiency. Essentially, it’s the invisible nervous system of your home, connecting everything from your thermostat to your security cameras.
Fundamental Components of a Smart Home Network
A smart home network typically consists of several key components working together. These include a router (often a Wi-Fi router), smart home hubs (sometimes acting as central controllers), various smart devices (lights, thermostats, locks, appliances), and the communication protocols that allow these devices to talk to each other. The router provides the primary internet connection, while hubs often simplify the management and communication between devices using different protocols.
Smart devices themselves vary greatly in functionality and capabilities.
Network Topologies in Smart Homes
Smart homes utilize different network topologies to connect devices efficiently. Two common topologies are star and mesh networks. In a star topology, all devices connect directly to a central hub. This is simple to set up and manage but can be vulnerable to single points of failure. If the hub fails, the entire network is affected.
A mesh network, on the other hand, uses multiple nodes to create a self-healing network. Devices connect to the nearest node, creating multiple paths for data transmission. This makes the network more resilient and provides better coverage, especially in larger homes.
Wired and Wireless Communication Protocols
Smart home networks employ both wired and wireless communication protocols. Wired connections, typically using Ethernet cables, offer higher bandwidth and greater reliability, making them suitable for devices requiring consistent and high-speed data transfer, such as security cameras with high-resolution video streaming. Wireless connections, utilizing technologies like Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Bluetooth, provide flexibility and ease of installation, ideal for most smart home devices.
However, wireless connections are susceptible to interference and can experience lower bandwidth compared to wired connections. The choice between wired and wireless often depends on the specific device requirements and the home’s infrastructure.
Comparison of Common Smart Home Network Protocols
The following table compares common smart home protocols:
| Protocol | Range | Power Consumption | Data Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zigbee | Up to 100 meters (indoors) | Low | 250 kbps |
| Z-Wave | Up to 30 meters (indoors) | Low | 100 kbps |
| Wi-Fi | Varies depending on router and environment; generally up to 100 meters or more | Moderate to High | Varies greatly depending on standard; up to several gigabits per second |
| Bluetooth | Up to 10 meters | Low | 1 Mbps |
Security Considerations in Smart Home Networks
Source: buildingmaterialreporter.com
Smart homes, while offering convenience and automation, introduce new security vulnerabilities that need careful consideration. The interconnected nature of these systems creates potential entry points for malicious actors, ranging from unauthorized access to data breaches and even physical control of devices. Understanding these risks and implementing robust security measures is crucial for protecting your privacy and safety.
Smart home networks are susceptible to various attacks due to their reliance on internet connectivity and often less secure default settings. These vulnerabilities can expose sensitive data, allow unauthorized control of devices, and potentially compromise the entire home network. Effective security strategies involve a multi-layered approach encompassing device security, network security, and user awareness.
Smart home networks are transforming how we live, offering seamless control over various aspects of our homes. This extends to clever storage solutions, too, like optimizing space with the sleek and customizable Modular cabinets , which can even integrate with smart home systems for automated opening and closing. Ultimately, enhancing both convenience and aesthetics within your connected home environment.
Common Security Vulnerabilities in Smart Home Networks
Smart home devices frequently suffer from weak default passwords, lack of encryption, and insufficient software updates. These weaknesses allow attackers to easily gain access, potentially installing malware, stealing personal information, or even taking control of connected appliances. For example, a vulnerable smart thermostat could be remotely manipulated to cause discomfort or even damage, while a compromised security camera could be used for surveillance.
Outdated firmware often contains known vulnerabilities that hackers exploit, highlighting the importance of regular updates.
Securing Smart Home Devices and Networks
Strong passwords, unique for each device, are a fundamental security measure. Avoid easily guessable passwords and utilize password managers to generate and store complex credentials. Encryption protocols, such as WPA3 for Wi-Fi and TLS for data transmission, are vital for protecting data in transit and at rest. Regular software updates patch security flaws, mitigating potential vulnerabilities. Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification step beyond a password.
Smart home networks offer incredible convenience, automating tasks and improving efficiency throughout your house. This extends even to the garage; consider optimizing your space with Premium Garage Storage Cabinets to keep things organized and easily accessible. A well-organized garage contributes to a smoother, more efficient smart home system overall.
For example, using 2FA on your smart home hub prevents unauthorized access even if an attacker obtains your password. Finally, regularly review connected devices to remove any unnecessary ones.
Designing a Security Plan for a Typical Smart Home Network
A comprehensive security plan should start with device selection. Choose reputable brands with a strong track record of security updates and robust security features. Prioritize devices with strong encryption and support for 2FA. When configuring your network, use a strong and unique password for your router and enable WPA3 encryption. Regularly scan your network for unauthorized devices and change passwords periodically.
Consider segmenting your network, separating smart home devices from other devices like computers and laptops, to limit the impact of a potential breach. Implementing a firewall to control network traffic can also help prevent unauthorized access. Finally, establish a routine for regular software and firmware updates across all smart home devices.
Protecting Smart Home Networks from External Threats
External threats include malware, phishing attacks, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Keeping your devices and software updated is the first line of defense against many threats. Regularly monitor your network activity for suspicious behavior. A robust firewall can help prevent unauthorized access and block malicious traffic. Use a strong, unique password for your router and Wi-Fi network.
Smart home networks are revolutionizing how we interact with our homes, offering seamless control over lighting, appliances, and security. But even in a high-tech smart home, there’s still a place for classic design elements, like the beautiful craftsmanship you’ll find in Traditional cabinets. These timeless pieces add a touch of elegance that complements the modern convenience of smart home technology, creating a balanced and sophisticated living space.
Ultimately, a truly smart home integrates both cutting-edge technology and enduring style.
Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks to control your smart home devices, as this exposes your network to potential attacks. Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) for added security, especially when accessing your smart home network remotely. Educating all household members about potential threats and best practices is also crucial.
Interoperability and Standards
The dream of a truly seamless smart home, where all devices work together harmoniously, is hampered by a significant challenge: interoperability. Different manufacturers often use proprietary protocols and communication methods, preventing devices from easily communicating and sharing information. This lack of interoperability creates frustration for consumers, limiting the functionality and potential of their smart home systems. Addressing this issue requires a deeper understanding of the challenges and the role of open standards in creating a more unified smart home experience.The primary challenge in achieving interoperability lies in the fragmented nature of the smart home market.
Numerous companies offer a wide range of devices, each operating on its own ecosystem or using a unique set of protocols. This creates “siloed” systems where a smart light bulb from one manufacturer might not work with a smart thermostat from another. This incompatibility often necessitates the use of multiple apps and interfaces, leading to a complex and often frustrating user experience.
Furthermore, the rapid pace of innovation in the smart home sector means new devices and protocols are constantly emerging, further complicating the interoperability landscape.
Challenges Related to Interoperability Between Smart Home Devices and Platforms, Smart home networks
The lack of universal standards and protocols is the root cause of interoperability issues. Each manufacturer may employ different communication protocols (such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi), data formats, and security measures. This results in incompatibility between devices from different brands, making it difficult to integrate them into a single, cohesive system. For instance, a smart speaker may be unable to control a smart lock if they don’t share a common communication protocol or use incompatible security encryption.
Furthermore, differences in the user interfaces and control methods across various platforms can create confusion and hinder seamless integration.
The Role of Open Standards in Improving Interoperability
Open standards play a crucial role in addressing the interoperability challenge. They provide a common framework for device communication, enabling different manufacturers to create compatible products. Open standards are publicly available specifications that any company can use to develop devices. This ensures that devices from different manufacturers can communicate and interoperate seamlessly, regardless of their brand or platform.
The adoption of open standards reduces the reliance on proprietary protocols, promoting a more open and competitive smart home market. Examples of the benefits include simpler integration processes, broader device compatibility, and reduced vendor lock-in for consumers.
Comparison of Different Smart Home Ecosystems
Several prominent smart home ecosystems exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses regarding interoperability.
| Ecosystem | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Apple HomeKit | Strong focus on security and privacy, generally good interoperability within the ecosystem. | Limited device support compared to other ecosystems, requires Apple devices. |
| Google Home | Wide device support, robust voice control, integrates well with other Google services. | Security concerns have been raised in the past, some devices may not integrate perfectly. |
| Amazon Alexa | Extensive device compatibility, large user base, robust skill ecosystem. | Privacy concerns have been raised, interoperability can be inconsistent across devices. |
Existing Standards and Protocols Promoting Interoperability in Smart Home Networks
A number of standards and protocols aim to improve interoperability within smart home networks. These standards provide a common language for devices to communicate, enabling seamless integration and control. The widespread adoption of these standards is essential for creating a truly unified smart home experience.
- Zigbee: A low-power, mesh networking protocol widely used for smart home devices such as lighting and sensors.
- Z-Wave: Another low-power, mesh networking protocol commonly used for home automation devices, known for its robust range and security features.
- Matter (formerly Project CHIP): A royalty-free, open standard developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance, aiming to unify different smart home protocols and improve interoperability across brands.
- Wi-Fi: While not exclusively a smart home protocol, Wi-Fi is a widely used standard for connecting smart home devices to the internet and each other.
- Bluetooth: Commonly used for connecting smaller, low-power devices like smart locks and sensors to smartphones and other hubs.
Network Performance and Optimization
A smoothly running smart home network is crucial for the seamless operation of all your connected devices. However, various factors can impact performance, leading to frustrating delays, connectivity issues, and overall system instability. Understanding these factors and implementing optimization strategies is key to a happy, connected home.Network performance in a smart home hinges on several key aspects: bandwidth, latency, and interference.
Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over your network at any given time. Insufficient bandwidth can lead to slowdowns, especially when multiple devices are streaming or downloading simultaneously. Latency, or delay, measures the time it takes for data to travel between devices. High latency results in sluggish responsiveness, impacting everything from video calls to smart home automation commands.
Smart home networks are transforming how we interact with our homes, offering seamless control over lighting, temperature, and even security. This extends to the bathroom, where you can integrate smart features into your design; for instance, consider incorporating Luxury Bathroom Cabinets with built-in smart mirrors or lighting systems. Ultimately, a well-designed smart home network enhances convenience and elevates the overall living experience.
Finally, interference from other electronic devices, such as microwaves or cordless phones, can disrupt Wi-Fi signals, causing dropped connections and reduced speeds.
Factors Affecting Smart Home Network Performance
Bandwidth limitations, high latency, and signal interference are the primary culprits behind poor smart home network performance. Consider a scenario with multiple users streaming 4K video, while smart lights, security cameras, and smart appliances are constantly sending and receiving data. This high demand can quickly overwhelm a network with limited bandwidth, resulting in buffering, slow loading times, and potentially even device disconnections.
Similarly, interference from neighboring Wi-Fi networks or electronic devices operating on the same frequency can weaken signals, increasing latency and causing unreliable connections. This is particularly problematic for devices located further away from the router or in areas with physical obstructions.
Methods for Optimizing Smart Home Network Performance
Optimizing your smart home network involves a multi-pronged approach. Firstly, upgrading to a router with a higher bandwidth capacity and a more powerful signal can significantly improve performance. Consider a mesh Wi-Fi system for larger homes to ensure consistent coverage throughout. Secondly, strategically placing your router and Wi-Fi extenders minimizes signal interference and dead zones. Avoid placing the router near metal objects or appliances that might disrupt the signal.
Thirdly, regularly updating your router’s firmware ensures it operates with the latest security patches and performance enhancements. Finally, employing Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router allows you to prioritize bandwidth for specific devices or applications, such as video streaming or online gaming, ensuring they receive sufficient bandwidth even during periods of high network activity.
Impact of Network Congestion on Smart Home Device Functionality
Network congestion, caused by excessive data traffic, significantly impacts smart home device functionality. Smart lights might flicker or fail to respond to commands, security cameras may experience lag or dropped frames, and smart appliances could malfunction or exhibit erratic behavior. Streaming services will buffer constantly, and video calls will become choppy and unreliable. In extreme cases, network congestion can lead to complete device unresponsiveness or disconnections.
The severity of the impact depends on the level of congestion and the individual device’s sensitivity to network conditions. For instance, a smart thermostat might tolerate minor network delays more effectively than a security system relying on real-time video streaming.
Troubleshooting Common Network Connectivity Issues
Troubleshooting smart home network issues often involves a systematic approach. Begin by checking the obvious: ensure your devices are powered on and correctly connected to the network. Then, restart your router and modem to clear any temporary glitches. If the problem persists, examine your network’s bandwidth usage using your router’s administration interface or a network monitoring tool.
This can help identify devices consuming excessive bandwidth. Check for signal interference by moving devices closer to the router or using a Wi-Fi extender. Finally, if the issue is isolated to a specific device, try resetting it to factory settings or consulting the device manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide. If problems persist after these steps, consider contacting your internet service provider for assistance.
Smart Home Network Scalability and Future Trends

Source: fastcabling.com
Smart home networks are transforming how we live, offering seamless control over everything from lighting to security. Integrating these systems into your home design is key, and showcasing your smart devices beautifully can be achieved by using stylish storage solutions, like the stunning Luxury Display Cabinets which add a touch of elegance while keeping your tech organized.
This way, your smart home network isn’t just functional, but a visually appealing part of your home’s aesthetic.
The increasing popularity of smart home devices presents a significant challenge: scaling home networks to handle the growing number of connected gadgets without compromising performance or security. As more devices join the network – from smart lights and thermostats to security cameras and appliances – the strain on bandwidth, processing power, and network infrastructure becomes more pronounced. This necessitates a forward-looking approach to smart home network architecture and the adoption of emerging technologies.Smart home networks face several scalability hurdles.
Bandwidth limitations can lead to slow response times and dropped connections, especially with bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming from multiple security cameras. Network congestion becomes a major issue as the number of devices competing for network resources increases. Moreover, managing and securing a large number of devices requires sophisticated network management tools and robust security protocols. The complexity of the network increases exponentially with each new device, potentially leading to configuration errors and vulnerabilities.
Challenges of Scaling Smart Home Networks
Scaling a smart home network effectively requires addressing several key challenges. First, the network infrastructure itself needs to be robust enough to handle the increased traffic. This might involve upgrading to a faster internet connection (e.g., fiber optics), implementing a mesh Wi-Fi system for better coverage and stability, or employing advanced network technologies like Wi-Fi 6E or Thread. Second, device management becomes more complex with a large number of devices.
Centralized management systems and automated configuration tools are crucial for simplifying the process. Third, security becomes paramount. A larger network presents a larger attack surface, requiring robust security protocols and regular updates to protect against vulnerabilities.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Future Smart Home Networks
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize smart home networks. AI-powered network management systems can optimize network performance by dynamically allocating bandwidth, identifying and resolving bottlenecks, and proactively detecting and mitigating security threats. AI can also personalize the smart home experience by learning user preferences and automating tasks accordingly. The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, driving the need for more sophisticated network architectures.
Technologies like Thread and Matter are aiming to improve interoperability and simplify device integration, making it easier to scale a smart home network without encountering compatibility issues. Furthermore, edge computing – processing data closer to the source (the devices themselves) – will reduce reliance on cloud services, improving response times and enhancing privacy.
Cloud-Based Services for Smart Home Management: Benefits and Drawbacks
Cloud-based services offer centralized management, remote access, and advanced features like voice control and automation. However, they also raise concerns about data privacy and security. Reliance on cloud services introduces a single point of failure, and data breaches could compromise sensitive information about home activities and preferences. On the other hand, cloud services can provide scalability and cost-effectiveness, as they handle the complex task of managing a large number of devices.
A hybrid approach, combining on-premise infrastructure with cloud services, might offer a balanced solution, maximizing the benefits while mitigating the risks.
Evolution of Smart Home Network Architectures
A visual representation of the evolution would show a progression from simple star topologies (a single router connecting all devices) in early smart homes, to more complex mesh networks with multiple access points providing broader coverage and redundancy. The next stage would illustrate the integration of edge computing devices, distributing processing power and reducing reliance on the cloud. Finally, the future architecture would depict a highly decentralized and AI-powered network, with intelligent devices autonomously managing resources and adapting to changing conditions, potentially leveraging technologies like blockchain for enhanced security and trust.
Smart Home Network Deployment and Management
Setting up and maintaining a robust smart home network is crucial for a seamless and enjoyable experience. This involves careful planning, proper configuration, and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance and security. This section details the steps involved in deploying and managing your smart home network effectively.
Setting Up a Smart Home Network
Establishing a reliable smart home network begins with a solid foundation. This includes choosing the right router, understanding your network’s capabilities, and planning for future expansion. First, assess your home’s size and the number of smart devices you plan to connect. A larger home or a greater number of devices will require a more powerful router with a wider range and greater bandwidth capacity.
Consider routers with features like mesh networking for extended coverage and better performance in larger spaces. Next, select a router with sufficient Ethernet ports for wired connections to devices requiring higher bandwidth, such as streaming devices or gaming consoles. Wireless connectivity (Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E) is essential for most smart devices, and a strong, stable Wi-Fi signal is paramount.
Finally, ensure your internet connection speed is adequate to support all your connected devices. A faster internet connection will improve the overall performance and responsiveness of your smart home network.
Configuring a Smart Home Router for Optimal Performance
Optimizing your smart home router is key to maximizing its capabilities and ensuring all devices function efficiently. This involves several steps to enhance security, improve performance, and ensure network stability. Begin by changing the default router password to a strong, unique password. This is crucial for security. Next, enable WPA3 or WPA2 encryption for your Wi-Fi network to protect against unauthorized access.
Regularly update your router’s firmware to patch security vulnerabilities and improve performance. Consider creating separate guest networks to isolate your primary network from potentially insecure devices. For better performance, choose the appropriate Wi-Fi channel and band. Using a Wi-Fi analyzer tool can help identify less congested channels. If your home is large, consider using a mesh Wi-Fi system for broader coverage and improved signal strength throughout your home.
Finally, regularly monitor your router’s performance using the router’s administration interface or third-party network monitoring tools. This helps identify and address any potential issues before they impact your smart home devices.
Managing and Maintaining a Smart Home Network
Ongoing management ensures your smart home network remains efficient and secure. This includes regular monitoring, software updates, and proactive problem-solving. Regularly check your router’s logs for any errors or unusual activity. This can help identify potential security breaches or performance bottlenecks. Update the firmware of your router and all your smart devices regularly to ensure they have the latest security patches and performance enhancements.
Consider using a network management application to monitor your network’s performance, identify slow devices, and manage bandwidth allocation. This provides a centralized view of your network’s health and performance. Regularly back up your network configuration settings in case of unexpected issues. This ensures you can quickly restore your network to its previous state. Finally, regularly review your network security settings to ensure they are up-to-date and effective.
This helps protect your smart home network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Troubleshooting Common Smart Home Network Problems
A checklist can assist in diagnosing and resolving common issues. Proactive troubleshooting can save time and frustration.
- Device Offline: Check device power, Wi-Fi connection, and router connectivity. Reboot the device and router.
- Slow Network Speed: Check internet speed, router congestion, and interference from other devices. Consider upgrading your internet plan or router.
- Poor Wi-Fi Signal: Check router placement, interference from walls and appliances, and consider using a Wi-Fi extender or mesh system.
- Security Issues: Change router password, enable strong encryption (WPA3/WPA2), update firmware, and regularly scan for malware.
- Network Unresponsive: Reboot your router and modem. Check for any power outages affecting your internet service.
- Device Incompatibility: Verify device compatibility with your network and other smart home devices. Check for firmware updates.
- Smart Home App Issues: Check app permissions, update the app, and try reinstalling the app. Contact the app developer for support.
Ultimate Conclusion
Creating a truly smart home hinges on a well-designed and secure network. We’ve covered the essential components, from choosing the right protocols and securing your devices to optimizing performance and planning for future growth. Remember, a proactive approach to security and a clear understanding of your network’s capabilities are key to unlocking the full potential of your smart home.
By carefully considering the factors discussed, you can build a connected home that’s both efficient and secure, enhancing your lifestyle without compromising your privacy or safety. Embrace the future of home automation with confidence and enjoy the convenience a well-managed smart home network provides.
Popular Questions
What is the difference between Zigbee and Z-Wave?
Zigbee is generally cheaper and uses less power, but Z-Wave often boasts better range and reliability. The choice depends on your specific needs and the devices you’re using.
How can I improve my smart home network’s speed?
Consider upgrading your router to a newer model with better Wi-Fi capabilities, using a mesh network for wider coverage, and minimizing wireless interference from other devices.
Are my smart home devices vulnerable to hacking?
Yes, all connected devices are potentially vulnerable. Use strong, unique passwords, enable two-factor authentication where possible, and keep your devices’ firmware updated.
What should I do if my smart home devices are offline?
First, check your internet connection. Then, restart your router and the affected devices. If the problem persists, check for network congestion or interference and consider contacting your internet service provider or the device manufacturer.
How do I choose the right smart home hub?
Consider compatibility with your existing devices and desired features. Popular options include Amazon Alexa, Google Home, and Apple HomeKit, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.



